Choose a Trusted Validator
What is purposes of Staking?
Before staking your AURA, you should know that the purposes of staking are:
- Secure the chain: with Aura, everyone has the superpower to contribute to the security and participate in the governance of the Aura Network.
- Earn rewards: select one or more validators of the Aura Network and start earning AURA.
- Vote for the future: participants have the right to vote on proposals and make decisions on the future of the network.
Aura holders that do not operate validators themselves also can participate in securing the network by a mechanism called Delegation. When Aura holders stake their Aura, they must choose one or more trusted validators to delegate to. Validators are then able to receive rewards but are also be at risk of slashing if the validators they chose misbehave. Before Aura holders start the staking process, they must setup their wallet, transfer Aura to the wallet and then select trusted validators.
Select trusted Validators
Click Validators in the menu to view Validators list of the network.
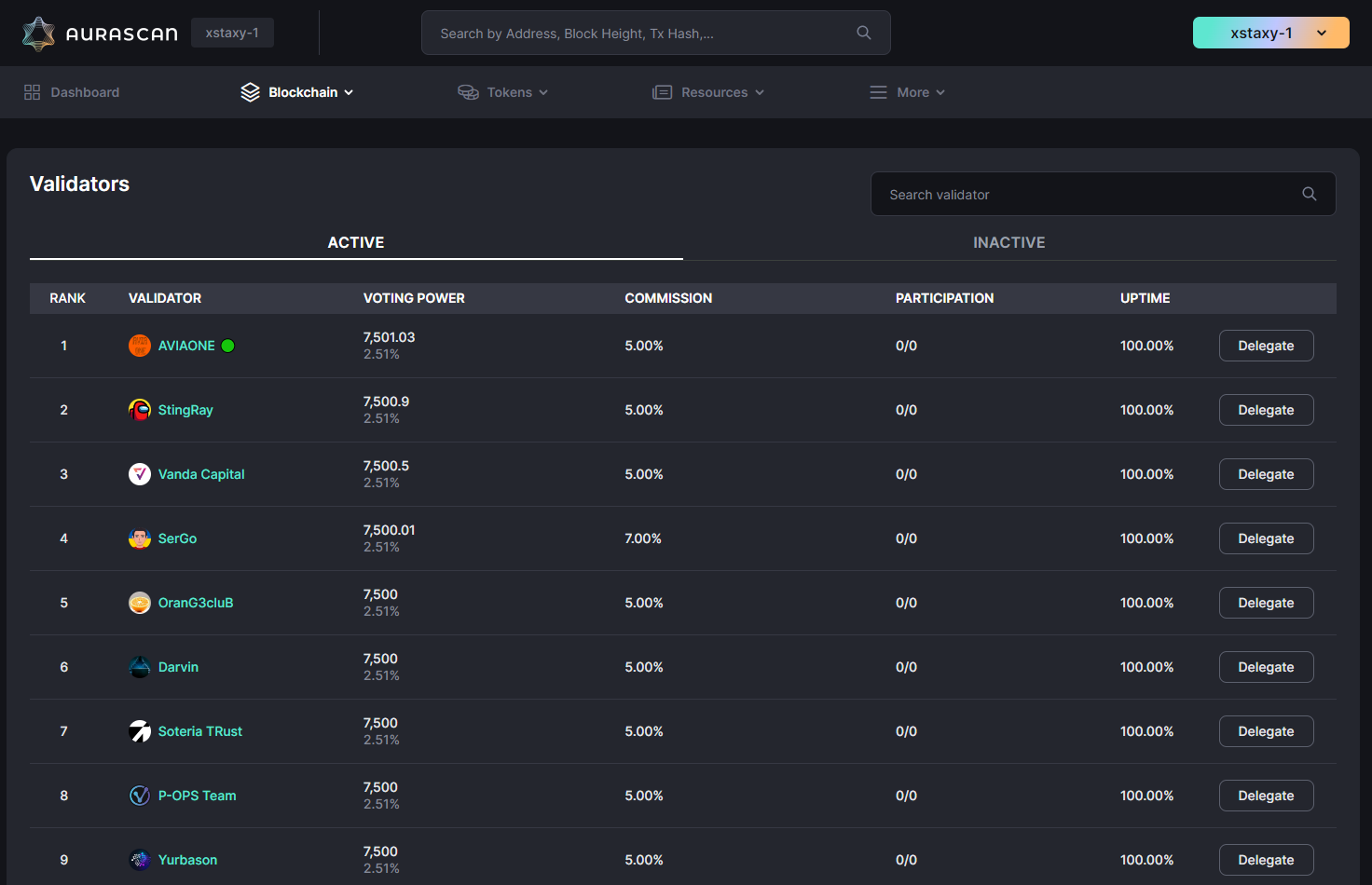
Aura holders have access to a range of Validators information available in Aura network explorers like Aurascan. Please review the following information before staking:
- Validator name: also known as the moniker
- Voting power: the sum of self-bonded and delegated tokens
- Commission: validator service fee charged to delegators
- Participation: vote participation stat for proposals
- Uptime: proportion of the period of time that validator's server was used without any problems
Aura holders should research and learn more about a validator's operation, history and security practices to choose a trusted validator to prevent slashing.
Validator details
When choosing a validator, you can view the Validator information details included in the Validator profile, Proposed Blocks, Uptime, Delegators and Power Events.
- Validator profile The basic information of validator:
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator Address | Validator operator address at which Aura holders delegate their voting power to |
| Address | Personal wallet address of a validator |
| Website | Website of the validator's organization |
| Commission | Validator service fee charged to delegators |
| Uptime | Proportion of the period of time that validator's server was used without any problems |
| Voting Power | The sum of self-bonded and delegated tokens |
| Bonded Height | The block height at which validator was bonded |
| Self Bonded | The delegation of Aura from a validator to themselves |
| Details | Details information of the validator |
- Proposed Blocks The validator that is selected to propose the next block is called the proposer. Proposed blocks is the blocks list that the validator proposed.
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Height | The block height that the validator proposed. Click the block height to view block details |
| Block Hash | Hash of the block |
| Txs | Number of transactions inside the block |
| Time | Timestamp that block is on-chain |
Uptime View the last 100 blocks, missed blocks are displayed with an X
Delegators List of delegators that delegated to the validator
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Delegator Address | Wallet address of delegator |
| Amount | Amount of AURA that delegator delegated to validator |
- Power Events Transactions list related to Operator Address (when delegator delegate/undelegate/redelegate from/to validator)
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Height | The block height of this transaction |
| TxHash | Hash of transaction |
| Amount | Amount that delegator delegate/undelegate/redelegate from/to validator |
| Time | Timestamp of transaction |